Output and employment in Construction and related industries
There is no specific definition of an industrial sector. It is a broad collection of firms from different industries, for example ‘agriculture’ includes cropping, grazing, forestry and fishing, or the many ‘manufacturing’ industries like chemicals, plastics, steel and textiles. Firms in an industrial sector are too diverse and geographically distributed to be called an industry cluster, and this is the case for the dense network of firms involved in constructing, managing and maintaining the built environment. The collective significance of these firms from different industries is obscured by their diversity, ranging from architecture to waste disposal, and their geographic distribution, but together they are one of the largest and most important industrial sectors in the economy.
The industries that make up the Australian Built Environment Sector (BES) are involved in construction of buildings and structures, supply of materials, machinery and equipment, provision of professional services in design, engineering and surveying, management of water and waste, and maintenance of buildings. Combining them into an industrial sector provides perspective on their economic role and significance.
The analysis is based on data from the annual Australian Bureau of Statistics publication Australian Industry, using industry value added (IVA) and industry employment in June. IVA is the estimate of an industry’s annual output and its contribution to gross domestic product (GDP), and is broadly the difference between total income and total expenses. IVA is given in current prices in Australian Industry (i.e. not adjusted for inflation), therefore growth in IVA reflect changes in both prices paid for goods and services and the quantity of output. The data begins in 2006-07 and the most recent issue is 2023-24
Economies grow by upgrading the products they produce, but the technology, capital, institutions, and skills needed to make newer products are more easily adapted from related products with common labour and capital requirements. This network of relatedness means the set of options available for an industry are strongly influenced by its current product space. With new production technologies such as 3D printing of concrete, automated machinery and equipment, and prefabrication with engineered wood, the BES is a laboratory for the fourth industrial revolution.
Taking a broad view of an industrial sector provides perspective on its role and significance in economic and technological development. When economic activities are spread across a wide range of individual industries the contribution of the whole is not obvious. This is why the tourism industry has an annual ABS TourismSatellite Account that brings together the contributions of industries like accommodation, tour operators and entertainment to estimate their total output and employment, which in 2023-24 was 2.9 percent of GDP and 4.4 percent of employment. The BES is over four times the size of tourism, and should have a satellite account of its own to provide more and better data for policies affecting construction of housing, infrastructure and other buildings [1].
Industries Included in the Australian Built Environment Sector
There are nine built environment industries included in the BES. In the industry classification system the ABS uses, eight of these are subdivisions (e.g. Construction has three subdivisions, and Non-metallic mining and quarrying is a subdivision of Mining), and Manufacturing is a division. Subdivisions are made up of industry classes (e.g. trades are classes within the subdivision of Construction services, and Architectural, Surveying and Engineering services are three classes in the non-IT subdivision of Professional, technical and scientific services). Australian Industry has data for Manufacturing industry classes like Structural steel, Cement and Glass products, but for all other industries data is at the subdivision level [2].
The industry subdivisions and classes included are:
· Non-metallic mineral mining and quarrying, includes construction material mining;
· Water supply, sewerage & drainage services;
· Building construction, includes Residential and Non-residential contractors;
· Heavy and civil engineering, includes Road and bridge construction and other Heavy and civil engineering;
· Construction services, includes 19 industry trade classes;
· Property operators and real estate services, includes Residential and Non-residential operators, and Real estate services;
· Professional, technical and scientific services (except computer design and related services), includes Architectural, Surveying and Engineering services;
· Building, cleaning, pest control and other services, includes Gardening services;
· Manufacturing industries, includes 17 classes.
The boundaries around these subdivisions are not perfectly aligned with the built environment, so there is a bit of give and take in the data. For example, Non-metallic mineral mining and quarrying includes activities such as opal mining that are not related to the built environment. On the other hand, there are classes in subdivisions that are too broad to be included, despite their importance in construction and maintenance of the built environment. For example rental of heavy machinery and scaffolding is in a subdivision of Rental, hiring and real estate services but the data is not available.
Contribution of the Built Environment Sector to the Australian Economy
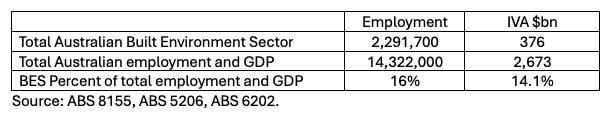
In 2023-24, the BES employed 2,291,700 million people and the share of total employment was 16 percent. Since 2006-07 the BES share of total employment has been around 16 percent, except for 2010 and 2013 when it was 15 and 14 percent respectively. In 2023-24, the BES produced $376 billion in IVA, contributing 14.1 percent to nominal Australian GDP, and has been between 13 and 14 percent of GDP since 2006-07. The IVA per employee of the BES was $164,000 in 2023-24, compared to GDP per employee of $186,000.
Table 1. Built Environment Sector Contribution to the Australian Economy 2023-24
Figure 1. Percent share of Australian employment and output
Source: ABS 8155, 5206, 6202.
There have been three growth spikes in BES employment since 2006-07. The first was after the 2008-09 financial crisis with the Commonwealth Government’s education building program, the second in the mid-2010s during the apartment building boom, and the third during the pandemic with the Homebuilder program.
Figure 2. Annual change in employment
Source: ABS 8155, 6202.
Output of the BES has tracked GDP over time, in a similar pattern to employment. BES IVA grew faster than GDP in 2009-10 and between 2014 and 2016, but between 2017 and 2021 grew slightly less than GDP. The increase in inflation after 2021is clearly shown in Figure 3, which is in current prices and not adjusted for the inflationary effects on the supply chain.
Figure 3. BES IVA and GDP at current prices
Source: ABS 8155, 5206.
Contribution of Industries to the BES
There have been changes in the composition of the BES since 2006-07. Manufacturing has fallen from 9 percent of employment and 10.5 percent of IVA to 6 percent for both in 2023-24. Employment has increased by 2 percent for total Construction and 1 percent for Services, and IVA for Quarrying and Water, sewerage, drainage and waste has increased by 4 percent.
The tables below have the number of people employed in June 2024, the IVA for 2023-24 and IVA per employee for industries in the BES. IVA per employee is a broad indicator of productivity, although not precise it allows comparison between the labour intensive subdivisions like Building services and the capital intensive subdivisions like Quarrying.
Construction Industry
The construction industry is the core of the sector, making up 56 percent of BES employment, and 47 percent of BES IVA in 2023-24. Within Construction, the shares of Building and Engineering have increased while Construction services has declined. As Figure 4 shows, the relationship between the share of BES employment and the share of BES IVA is markedly different, with Construction services having a much larger share of employment of 38.5 percent than IVA at 27.3 percent in 2023-24, for Building the shares were 11.1 percent of both employment and IVA, and for Engineering the shares were 6.7 percent of employment and 8.7 percent of IVA.
Figure 4. Construction subdivision shares of employment and output
Source: ABS 8155.
Table 2. Construction subdivisions 2023-24
Service Industries
Services are provided by BES classes within the subdivisions of Property operators and real estate, Professional, technical and scientific services (except computer design and related services), and Building, cleaning and pest control. The combined share of the BES for the three subdivision in 2023-34 was 35 percent of employment and 38.5 percent of IVA.
The share of the BES of Property operators and real estate employment was 14 percent but the subdivision had a higher IVA share of 24 percent in 2023-24. The employment and IVA shares for the Architectural, Engineering and Surveying services in the Professional, technical and scientific services subdivision were both 11 percent. Building, cleaning and pest control had a much larger share of employment at 9 percent than IVA of 4 percent.
Figure 5. Service industry subdivision shares of employment and output
Source: ABS 8155.
Table 3. Service industry subdivisions 2023-24
Quarrying, Water and Manufacturing
There are three capital intensive industries in the BES: Manufacturing (discussed below), Quarrying, and Water, sewerage, drainage and waste. Figure 6 shows the Quarrying and Water subdivisions have significantly higher shares of IVA than employment because of the high level of capital stock in those industries, made up of machinery and equipment in Quarrying, and physical infrastructure and equipment for Water etc. There was a very large increase in Quarrying IVA in the data for 2022-23 that has been carried into 2023-24 that is not explained by the ABS, but is probably due to a reclassification of a firm from another mining subdivision or industry. Manufacturing has declined from 9 percent of employment and 11 percent of IVA to 6 percent of both in 2023-24.
Figure 6. Capital intensive industry subdivision shares of employment and output
Source: ABS 8155.
Table 4. Quarrying, Water and Manufacturing 2023-24
BES Manufacturing
Seventeen Manufacturing industry classes are included in the Australian Built Environment Sector, and in 2023-24 there were 147,776 people employed in these industries. Figure 7 shows BES Manufacturing output and employment since 2006-07. The rise in prices during 2021 and 2022 is clearly seen in IVA. The industry classes included in BES Manufacturing are in Table 5.
Figure 7. BES Manufacturing output and employment
Source: ABS 8155.
Table 5 has the number of people employed, IVA per employee in 2023-24 and their change in employment since 2006-07. Three classes have had small decreases in employment, but employment has fallen by 36 percent for Clay brick manufacturing. The two manufacturing classes that have grown the most are Prefabricated wooden buildings and prefabricated metal building, both by 72 percent since 2006-07,although the former is a much smaller class than the latter.
Cement and lime manufacturing has the highest IVA per employee of $389,000, with Glass and Plaster products and Clay bricks the other high IVA per employee classes. The four classes with low IVA per employee were Veneer and plywood, Architectural aluminium, Metal roof and guttering and Other structural metal products.
Table 5. BES Manufacturing 2023-24
Figure 8 shows there are significant differences in the size of Manufacturing classes with products used in the BES. The three largest in 2023-24 by both employment and IVA were Wooden structural fittings and components, Structural steel, and Architectural aluminium. The smallest were Prefabricated wooden buildings, Veneer and plywood manufacturing, Clay bricks, and Plaster products.
Figure 8. BES Manufacturing classes IVA and employment
Source: ABS 8155.
Conclusion
This analysis uses data from the annual Australian Bureau of Statistics publication Australian Industry and combines data for industries that have a direct relationship with construction and the built environment. These industries make up the Australian Built Environment Sector (BES).
Onsite construction links suppliers of materials, machinery, equipment, products and components. Consultants provide design, engineering, cost planning and project management services. Once produced, buildings and structures need to be managed and maintained over their life cycle, work done by another group of related industries. The built environment also needs infrastructure and services like water and sewerage, provided by yet more industries. The collective significance of these industries is obscured by their diversity, ranging from architecture to waste collection, and their geographic distribution.
The economic role of the BES is significant. It accounted for 16 percent of total employment and BES Industry Value Added (IVA) was 14 percent of GDP in 2023-24. With a couple of exceptions, these shares have been constant since 2006-07 when the data begins. In 2023-24 BES IVA per employee was $164,000 compared to GDP per employee of $186,000.
The composition of the BES has changed slowly over time, as the percentage share of Manufacturing decreased from 10.5 percent of BES IVA and 9 percent of employment in 2006-07 to 6 percent for both in 2023-34. Employment has increased by two percent for total Construction and one percent for Services, and IVA for Quarrying and Water, sewerage, drainage and waste has increased by four percent.
Of the nine industries included in the Australian BES, three are from Construction, which accounted for 47 percent of BES IVA and 56 percent of BES employment. Within Construction, since 2006-07 the shares of Building and Engineering have increased while the Construction services share has declined.
Services are provided by Property operators and real estate, Professional, technical and scientific services (except computer design and related services), and Building, cleaning and pest control. The combined share of the BES for the three subdivisions in 2023-34 was 35 percent of employment and 38.5 percent of IVA.
There are two capital intensive industries in the BES, Quarrying, and Water, sewerage, drainage and waste. These subdivisions have significantly higher shares of IVA than employment because of the high level of capital stock in those industries, made up of machinery and equipment in Quarrying, and physical infrastructure and equipment for Water etc.
Seventeen manufacturing industry classes are included in the Australian Built Environment Sector, and in 2023 these employed 147,776 people with a combined IVA of $23 billion. The two manufacturing classes that have grown the most are Prefabricated wooden buildings and Prefabricated metal building, both by 72 percent since 2006-07, although the former is a much smaller class than the latter.
BES output and employment are useful indicators of the capacity constraints in construction of housing, infrastructure and other buildings, because the quantity of materials like gravel and concrete that can be produced in one year is limited, and the number of trades workers, engineers, project managers, and other workers, cannot be increased easily or quickly. This is only one of the many issues affecting construction, management and maintenance of the built environment.
These issues are wicked problems of great complexity that range widely across industries, institutions and regulatory systems. How measuring the BES helps is by providing an overview of the relatedness, scale and scope of these industries, their role in the value chain from suppliers to end users, and the possibilities for improving coordination between these industries. The built environment this industrial sector delivers is a major determinant of the quality of life, and how well the built environment functions depends on how well the BES can deliver the projects required.
[1] See Getting a broad view of constructing the built environment: A satellite account for built environment industries. In 2025 the ABS has new estimates for a quarterly Tourism satellite account, and a new 2023-24 satellite account for the Defence Industry (0.47% of national gross value added and 0.48% of employment) with Construction 13.2% of Defence GVA.
[2] Data on the industries included in the BES needs to be available at a level of detail that separates out BES components. This excludes industry divisions such as Transport and Financial services that clearly play a role in the BES, but that role cannot be identified in the data available for subdivisions. There are two industry subdivisions that can have their employment and IVA estimates weighted for the BES component, because the ABS occasionally releases supplementary tables that provide data at the industry class level. These are Professional, scientific and technical services (except computer design and related services), and Building cleaning, pest control and other services.
For Professional, scientific and technical services (except computer design and related services), in 2015-16 the combined share of the BES classes of Architectural services, Surveying and mapping services, and Engineering services in the subdivision were 24% of total employment and 28% of IVA. In 2016-17 data was provided for Administrative and support services, with the three BES classes Building and other industrial cleaning, Pest control, and Gardening services accounting for 95% of the subdivision’s total employment and 92% of IVA.
Australian Industry is produced annually using a combination of directly collected data from the ABS Economic Activity Survey and Business Activity Statement data provided by businesses to the Australian Taxation Office. The data includes all operating business entities, including non-profits, and Government owned or controlled Public Non-Financial Corporations. Excluded are entities classified to General government, Finance and insurance services, and Public administration and Defence.